
Tatyana Sandalova
Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
Title: Structural bases underlying re-established recognition of a viral immune escape variant
Biography
Biography: Tatyana Sandalova
Abstract
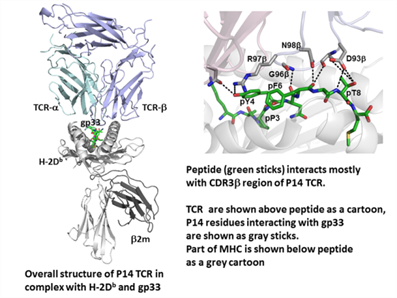
MHC-I molecules play a crucial role in immune surveillance by selectively presenting intracellular peptides at the cell surface to CD8+ T lymphocytes, including cytotoxic T lymphocytes, via T cell receptors (TCRs). Recognition of MHC/peptide complexes by TCRs is a critical event in initiation of immune responses. The T cell clone P14 is specific for H-2Db in complex with the Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-derived epitope gp33 (KAVYNFATM). The virus escapes immune recognition by modifying peptide position 4 to phenylalanine (Y4F). Using a combination of structural biology and immunology, we have defined a novel procedure that allows for the design of super-peptides that bind with high affinity to MHC-I. This discovery provides a powerful tool for improving vaccination. The highly immunogenic super-peptides act as mimotopes of disease-associated non-immunogenic epitopes. The increased immunogenicity induces T cell responses of a magnitude never before observed and our results demonstrate that the induced CD8+ T cells cross-react with the original peptides, resulting in enhanced in vitro and in vivo responses. Here we present for the first time the crystal structure of P14 in complex with H-2Db bound to five different peptides, providing a structural basis for our methodology. All five ternary structures revealed virtually the same TCR interface and contacts with an average RMSD of 0.45 Å2. Both the Vα and Vβ domains of P14 contribute equally to the interaction with H-2Db. In contrast to many others, no contacts are formed between CDR2α and H-2Db. Instead, several contacts are formed between the CDR3a residues Y101α and E104α and the H-2Db residues R62, K66 and E163. Three residues of gp33, pY4, pF6 and pT8 interact with CDR3β. R97β located at the tip of CDR3β interacts with both bulky residues of peptide, pY4 and pF6, and pT8 interacts with D93β.
References:
1. Hafstrand I, Doorduijn EM, Duru AD, Buratto J, Oliveira CC, Sandalova T, van Hall T, Achour A. The MHC Class I Cancer-Associated Neoepitope Trh4 Linked with Impaired Peptide Processing Induces a Unique Noncanonical TCR Conformer. J Immunol. 2016;196:2327-34.
2. Uchtenhagen H, Abualrous ET, Stahl E, Allerbring EB, Sluijter M, Zacharias M, Sandalova T, van Hall T, Springer S, Nygren PÅ, Achour A. Proline substitution independently enhances H-2D(b) complex stabilization and TCR recognition of melanoma-associated peptides. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43:3051-60.
3. Allerbring EB, Duru AD, Uchtenhagen H, Madhurantakam C, Tomek MB, Grimm S, Mazumdar PA, Friemann R, Uhlin M, Sandalova T, Nygren PÅ, Achour A. Unexpected T-cell recognition of an altered peptide ligand is driven by reversed thermodynamics. Eur J Immunol. 2012; 42:2990-3000.
4. Madhurantakam C, Duru AD, Sandalova T, Webb JR, Achour A. Inflammation-associated nitrotyrosination affects TCR recognition through reduced stability and alteration of the molecular surface of the MHC complex. PLoS One. 2012;7:e32805.
5. Grunewald J, Kaiser Y, Ostadkarampour M, Rivera NV, Vezzi F, Lötstedt B, Olsen RA, Sylwan L, Lundin S, Käller M, Sandalova T, Ahlgren KM, Wahlström J, Achour A, Ronninger M, Eklund A. T-cell receptor-HLA-DRB1 associations suggest specific antigens in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2016;47:898-909.
