Parisa Amirkalvanagh
Tarbiat Modares University, Iran
Title: Preparation and characterization of PLGA nanoparticles containing plasmid DNA encoding human IFN-lambda-1: Beginning for promising researches
Biography
Biography: Parisa Amirkalvanagh
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: During the last 15 years since the discovery of type III human interferons (IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3), numerous biological activity of these new interferon family has been introduced by researchers. Furthermore, several studies have showed that the encapsulation of plasmid DNA with nanoparticle result to protection of plasmid DNA against DNase enzyme and increasing gene delivery to the cells. So we decided to encapsulate plasmid DNA encoding IFN-λ1 with PLGA in order to compare encapsulated and naked form of plasmid DNA encoding IFN-λ1 in the future researches.
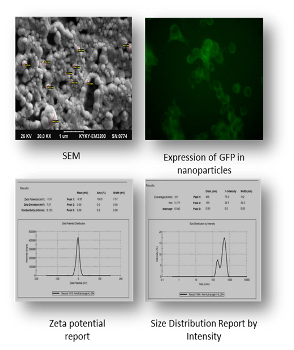
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: At first, the expression and bioactivity of pIFN-λ1 was investigated in vitro by sandwich ELISA and CPER assay, respectively. Then, pIFN-λ1 was encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles using double emulsion-solvent evaporation method and characterized in terms of size, zeta potential and polydispersity index (DLS), morphology (SEM) and encapsulation efficiency and release kinetics. Uptake of nanoparticles by RAW264.7 macrophages was also studied by fluorescent microscope.
Findings: IFN-λ1 expressed in HEK293T was confirmed by sandwich ELISA and IFN-α2b was able to protect HEP2 cells against VSV infection. Developed nanoparticles were spherical in shape with a mean diameter of 381 nm (PdI: 0.279), encapsulation efficiency was 75±5% and a zeta potential of -3.35±7.75 mV was observed. Release assay in vitro showed that the plasmid DNA could be sustainably released from nanoparticles. Not only the successful expression of plasmid DNA encoding GFP revealed that nanoparticle could be engulfed by macrophages, but it also represented that the integrity of plasmid has been intact during encapsulation process.
Conclusion & Significance: Given the results in order to figure out the other new functions of this molecule or re-evaluation of previous investigations, using prepared and characterized nanoparticles instead of naked plasmids seems to be practically feasible.
References:
1. Rahimi, R, Ebtekar, M, Moazzeni, S.M, Mostafaie, A, Mahdavi, M (2015) Optimization of multi-epitopic HIV-1 recombinant protein expression in prokaryote system and conjugation to mouse DEC-205 monoclonal antibody: Implication for in-vivo targeted delivery of dendritic cells. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 18:145-152.
2. Hartoonian, C, Sepehrizadeh, Z, Tabatabai Yazdi, M, Jang, Y.S, Langroudi, L, Amir Kalvanagh, P, Negahdari, B, Karami, A, Ebtekar, M, Azadmanesh, K (2014) Enhancement of immune responses by co-delivery of CCL19/MIP-3beta chemokine plasmid with HCV core DNA/protein immunization. Hepatitis Monthly 14.
3. Hartoonian, C, Sepehrizadeh, Z, Mahdavi, M, Arashkia, A, Jang, Y.S, Ebtekar, M, Yazdi, M.T, Negahdari, B, Nikoo, A, Azadmanesh, K(2014) Modulation of hepatitis C virus core DNA vaccine immune responses by co-immunization with CC-chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) gene as immunoadjuvant. Molecular Biology Reports 41: 5943-5952.
4. Nikfarjam, B.A, Ebtekar, M, Sabouni, F, Pourpak, Z, Kheirandish, M(2014) Detection of interleukin-19 mRNA in C57BL/6 mice astroglial cells and brain cortex. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience 5: 88-95.
5. Yousefi, F, Ebtekar, M, Soleimani, M, Soudi, S, Hashemi, S.M(2013)Comparison of in vivo immunomodulatory effects of intravenous and intraperitoneal administration of adipose-tissue mesenchymal stem cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). International Immunopharmacology17: 608-616.
