
Reyhaneh Abgoon
Islamic Azad University, Iran
Title: Gene expression of PTPN-22 in Iranian patients with alopecia areata
Biography
Biography: Reyhaneh Abgoon
Abstract
Objective: In present study, effect of PTPN22 gene expression was investigated in Iranian AA patients and their respective controls.
Background: Alopecia areata (AA) is an autoimmune multifactorial disease characterized by hair loss especially from the scalp affecting approximately 5.3 million people. The gene encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22), which is exclusively expressed in immune cells, has been considered as a risk factor associated with the pathogenesis of AA.
Methods: The study group consisted of 30 patients with AA (13 female and 17 male, mean age 26.3±12.5) and 15 (5 female and 10 male, mean age 30±5.88) healthy controls. RNA was extracted from blood sample. Thereafter, cDNA was synthesized after RNA isolation. PTPN22 expression levels were measured by real-time PCR. Furthermore, association of this PTPN22 with some baseline clinical and demographical features was assessed.
Results: PTPN22 expression levels of patients with AA were significantly higher (4.6±3.8) than those in controls (1.14±0.56) (p value=0.01). PTPN22 expression was only associated with the sex of the AA patients (Fig.1).
Conclusion: In the present study, a significant association was found between PTPN22 gene expression and susceptibility to alopecia areata.
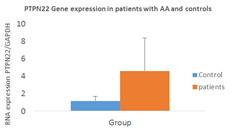
Figure1: PTPN22 gene expression in patients with Alopecia Areata and controls.
