
Azar Tahghighi
Pasteur Institute of Iran, Iran
Title: Design and synthesis of new heteroaromatic derivatives with anti-parasitic activity
Biography
Biography: Azar Tahghighi
Abstract
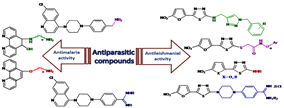
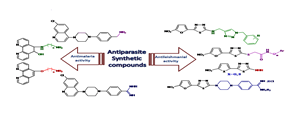
Parasitic diseases are a major problem in tropical and subtropical regions of the world such as malaria and leishmaniasis. These diseases cause considerable mortality and morbidity annually. No vaccines are available to prevent infections. On the other hand, parasitic drug resistances have restricted the use of available drugs for the treatment of malaria and leishmaniasis. Actually, identification and development of new, cheap, efficient, and safe compounds as drug candidates for the prophylaxis and treatment of these diseases are imperative from pharmaceutical point of view. Therefore, a range of creative strategies are required to achieve new lead compounds. The first aim of our studies were to synthesize and assess antileishmanial activity of 5-(5-nitrohetero aryl-2-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazoles with different substituents at the 2-position of thiadiazole ring. It was notable that the bioresponses and physicochemical properties of the molecules depended on the type of these substituents. In these studies, MLR and ANN models were used and predicted the antileishmanial activity of some thiadiazole derivatives. Also, molecular modeling and docking studies were conducted based on DNA topoisomerase as a target enzyme. The results suggested that hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions of ligands with the active site of Leishmania major topoisomerase IB were responsible for their potent antileishmanial activity. The other aim of our study was to synthesize a series of 1,10-phenanthroline derivatives containing amino-alcohol and amino-ether substituents, and quinoline derivatives containing benzyl dialkyl amine and N-alkyl benzamidine substituents. Their anti-plasmodial activity was then evaluated intraperitoneally using the Peter's 4-day suppressive test against Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Based on results, the synthetic compounds had about 90% suppression and also prolonged the mean survival time of treated mice in comparison with negative control groups.
References:
1. Parhizgar A R, Tahghighi A (2016) Introducing of new antimalarial analogues of chloroquine and amodiaquine: Narrative review. Iranaian Journal of Medical Science.
2. Tahghighi A, Dastmalchi S, Hamzeh-Mivehroud M, Asadpour-Zeynali K, Foroumadi A (2016) QSAR and docking studies on the (5-nitroheteroaryl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl) piperazinyl analogs with antileishmanial activity. Journal of Chemometrics 30: 284-293.
3. Tahghighi A (2014) Importance of metal complexes for development of potential leishmanicidal agents. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 770: 51-60.
4. Tahghighi A, Emami , Razmi S, Marznaki M R, Ardestani S K, Dastmalchi S, Kobarfard F, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2013) New 5-(nitroheteroaryl)-1,3,4-thiadiazols containing acyclic amines at C-2: Synthesis and SAR study for their antileishmanial activity. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry 28(4): 843-852.
5. Tahghighi A, Razmi S, Mahdavi M, Foroumadi P, Ardestani S K, Emami S, Kobarfard F, Dastmalchi S, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2012) Synthesis and anti-leishmanial activity of 5-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol- 2-amines containing N-[(1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl] moieties. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 50: 124-128.
