Zana Karimi Kurdistani
Pasteur Institute of Iran, Iran
Title: Association of miR-21 expression with gastric cancer in tissue and serum specimens of H. Pylori infected patients
Biography
Biography: Zana Karimi Kurdistani
Abstract
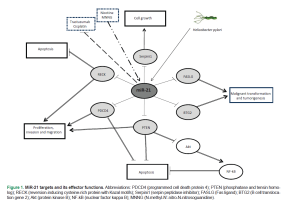
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fourth most prevalent cancer and the second most frequent cause of cancer death worldwide, with the higher mortality rate in developing country particularly in East Asia. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a recently discovered class of small, single-stranded non-coding RNA molecules, have been implicated in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. In total, serum of 70 patients with GC prior to any treatments and 70 healthy control subjects from Imam Khomeini Medical Center (Tehran, Iran) were provided in our study by the gastric cancer biobank at Pasteur Institute of Iran between 2014 and 2015. Serum miR-21 expression was significantly up-regulated in GC patients compared to healthy subjects (P=0.0023). After dividing GC patients into two early and late stages, this up-regulation maintained significant between late stage of GC patients and healthy subjects while this discrepancy was not statistically observed between early GC patients and healthy ones. Moreover, there was no significant difference between early and late stage (P>0.05). The Mann‑Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis tests showed that there were no marked correlation between the miR‑21 levels and factors such as age, gender, differentiation, lymph node metastasis, tumor size, venous invasion, tumor subsite, tumor type, tumor grade and tumor thickness (P>0.05). In conclusion, our analysis demonstrated that high expression of miR-21 in serum of GC samples involved in gastric cancer pathogenesis and its high level of presence has potential diagnostic value in screening for gastric cancer.